Time lapse: All Is Violent, All Is Bright
Updated: 2012-09-30 14:09:43
: , Subscribe Today Renew Give a Gift Archives Customer Service Facebook Twitter Newsletter SEARCH Health Medicine Mind Brain Technology Space Human Origins Living World Environment Physics Math Video Photos Podcast RSS SpaceFest IV interview Time lapse : All Is Violent , All Is Bright For this , the last day of the US Fiscal Year , here’s a lovely time lapse video from Tadas Janušonis , a photographer in Lithuania . It’s called All is Violent , All is Bright and features a series of interesting optical phenomena in the . sky Did you catch everything There were noctilucent clouds halos moondogs and a brief lunar corona But my favorite is the phenomenal oncoming storm starting three minutes in . That , or the giant spider at 2:40 clearly bent on destroying the world . I’m partial to stuff

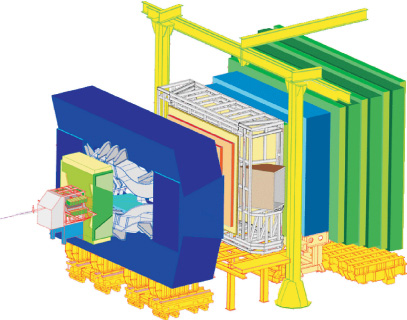 : Home Sitemap Contact us this site all CERN CERN European Organization for Nuclear Research The Large Hadron Collider About us Science Research The LHC People Why the LHC How the LHC works Heavy-ion physics The LHC Experiments ALICE ATLAS CMS LHCb TOTEM LHCf Computing The safety of the LHC Facts and figures LHC Milestones LHCb Large Hadron Collider beauty The LHCb experiment will help us to understand why we live in a Universe that appears to be composed almost entirely of matter , but no antimatter It specialises in investigating the slight differences between matter and antimatter by studying a type of particle called the beauty quark' , or b quark' . Instead of surrounding the entire collision point with an enclosed detector , the LHCb experiment uses a series of sub-detectors to
: Home Sitemap Contact us this site all CERN CERN European Organization for Nuclear Research The Large Hadron Collider About us Science Research The LHC People Why the LHC How the LHC works Heavy-ion physics The LHC Experiments ALICE ATLAS CMS LHCb TOTEM LHCf Computing The safety of the LHC Facts and figures LHC Milestones LHCb Large Hadron Collider beauty The LHCb experiment will help us to understand why we live in a Universe that appears to be composed almost entirely of matter , but no antimatter It specialises in investigating the slight differences between matter and antimatter by studying a type of particle called the beauty quark' , or b quark' . Instead of surrounding the entire collision point with an enclosed detector , the LHCb experiment uses a series of sub-detectors to Turn autoplay off Turn autoplay on Please activate cookies in order to turn autoplay off Jump to content s Jump to comments c Jump to site navigation 0 Jump to search 4 Terms and conditions 8 Edition : UK US Sign in Mobile Your profile Your details Your comments Your clippings Your lists Sign out Mobile About us About us Contact us Press office Guardian Print Centre Guardian readers' editor Observer readers' editor Terms of service Privacy policy Advertising guide Digital archive Digital edition Guardian Weekly Buy Guardian and Observer photos Today's paper The Guardian G2 features Comment and debate Editorials , letters and corrections Obituaries Other lives Sport Subscribe Subscribe Subscribe to the Guardian iPhone app iPad edition Kindle Extra Guardian Weekly Digital edition All our
Turn autoplay off Turn autoplay on Please activate cookies in order to turn autoplay off Jump to content s Jump to comments c Jump to site navigation 0 Jump to search 4 Terms and conditions 8 Edition : UK US Sign in Mobile Your profile Your details Your comments Your clippings Your lists Sign out Mobile About us About us Contact us Press office Guardian Print Centre Guardian readers' editor Observer readers' editor Terms of service Privacy policy Advertising guide Digital archive Digital edition Guardian Weekly Buy Guardian and Observer photos Today's paper The Guardian G2 features Comment and debate Editorials , letters and corrections Obituaries Other lives Sport Subscribe Subscribe Subscribe to the Guardian iPhone app iPad edition Kindle Extra Guardian Weekly Digital edition All our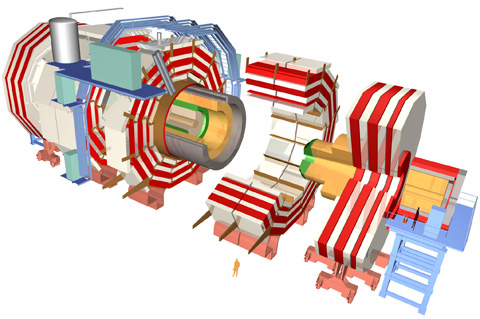 : Home Sitemap Contact us this site all CERN CERN European Organization for Nuclear Research The Large Hadron Collider About us Science Research The LHC People Why the LHC How the LHC works Heavy-ion physics The LHC Experiments ALICE ATLAS CMS LHCb TOTEM LHCf Computing The safety of the LHC Facts and figures LHC Milestones CMS Compact Muon Solenoid The CMS experiment uses a general-purpose detector to investigate a wide range of physics , including the search for the Higgs boson extra dimensions and particles that could make up dark matter Although it has the same scientific goals as the ATLAS experiment , it uses different technical solutions and design of its detector magnet system to achieve . these The CMS detector is built around a huge solenoid magnet . This takes the form of a
: Home Sitemap Contact us this site all CERN CERN European Organization for Nuclear Research The Large Hadron Collider About us Science Research The LHC People Why the LHC How the LHC works Heavy-ion physics The LHC Experiments ALICE ATLAS CMS LHCb TOTEM LHCf Computing The safety of the LHC Facts and figures LHC Milestones CMS Compact Muon Solenoid The CMS experiment uses a general-purpose detector to investigate a wide range of physics , including the search for the Higgs boson extra dimensions and particles that could make up dark matter Although it has the same scientific goals as the ATLAS experiment , it uses different technical solutions and design of its detector magnet system to achieve . these The CMS detector is built around a huge solenoid magnet . This takes the form of a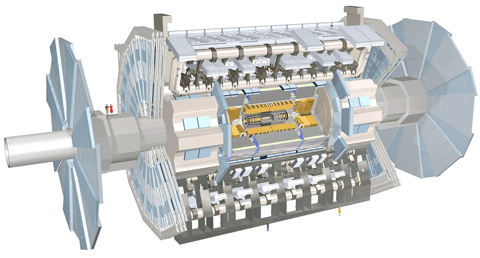 : Home Sitemap Contact us this site all CERN CERN European Organization for Nuclear Research The Large Hadron Collider About us Science Research The LHC People Why the LHC How the LHC works Heavy-ion physics The LHC Experiments ALICE ATLAS CMS LHCb TOTEM LHCf Computing The safety of the LHC Facts and figures LHC Milestones ATLAS ATLAS is one of two general-purpose detectors at the LHC . It will investigate a wide range of physics , including the search for the Higgs boson extra dimensions and particles that could make up dark matter ATLAS will record sets of measurements on the particles created in collisions their paths , energies , and their . identities This is accomplished in ATLAS through six different detecting subsystems that identify particles and measure their momentum and energy
: Home Sitemap Contact us this site all CERN CERN European Organization for Nuclear Research The Large Hadron Collider About us Science Research The LHC People Why the LHC How the LHC works Heavy-ion physics The LHC Experiments ALICE ATLAS CMS LHCb TOTEM LHCf Computing The safety of the LHC Facts and figures LHC Milestones ATLAS ATLAS is one of two general-purpose detectors at the LHC . It will investigate a wide range of physics , including the search for the Higgs boson extra dimensions and particles that could make up dark matter ATLAS will record sets of measurements on the particles created in collisions their paths , energies , and their . identities This is accomplished in ATLAS through six different detecting subsystems that identify particles and measure their momentum and energy  , Large Hadron Collider From Wikipedia , the free encyclopedia   (Redirected from LHC Jump to : navigation search LHC redirects here . For other uses , see LHC disambiguation Coordinates 46°14â²N 06°03â²E ï» ï» 46.233°N 6.05°E ï» 46.233 6.05 Large Hadron Collider LHC LHC experiments ATLAS A Toroidal LHC Apparatus CMS Compact Muon Solenoid LHCb LHC-beauty ALICE A Large Ion Collider Experiment TOTEM Total Cross Section , Elastic Scattering and Diffraction Dissociation LHCf LHC-forward MoEDAL Monopole and Exotics Detector At the LHC LHC preaccelerators p and Pb Linear accelerators for protons Linac 2 and Lead Linac 3 not marked Proton Synchrotron Booster PS Proton Synchrotron SPS Super Proton Synchrotron The Large Hadron Collider LHC is world's largest and highest-energy particle
, Large Hadron Collider From Wikipedia , the free encyclopedia   (Redirected from LHC Jump to : navigation search LHC redirects here . For other uses , see LHC disambiguation Coordinates 46°14â²N 06°03â²E ï» ï» 46.233°N 6.05°E ï» 46.233 6.05 Large Hadron Collider LHC LHC experiments ATLAS A Toroidal LHC Apparatus CMS Compact Muon Solenoid LHCb LHC-beauty ALICE A Large Ion Collider Experiment TOTEM Total Cross Section , Elastic Scattering and Diffraction Dissociation LHCf LHC-forward MoEDAL Monopole and Exotics Detector At the LHC LHC preaccelerators p and Pb Linear accelerators for protons Linac 2 and Lead Linac 3 not marked Proton Synchrotron Booster PS Proton Synchrotron SPS Super Proton Synchrotron The Large Hadron Collider LHC is world's largest and highest-energy particle , ATLAS experiment From Wikipedia , the free encyclopedia Jump to : navigation search ATLAS redirects here . For the linear accelerator , see Argonne Tandem Linear Accelerator System For other uses , see Atlas disambiguation Large Hadron Collider LHC LHC experiments ATLAS A Toroidal LHC Apparatus CMS Compact Muon Solenoid LHCb LHC-beauty ALICE A Large Ion Collider Experiment TOTEM Total Cross Section , Elastic Scattering and Diffraction Dissociation LHCf LHC-forward MoEDAL Monopole and Exotics Detector At the LHC LHC preaccelerators p and Pb Linear accelerators for protons Linac 2 and Lead Linac 3 not marked Proton Synchrotron Booster PS Proton Synchrotron SPS Super Proton Synchrotron Coordinates 46°14â²8â³N 6°3â²19â³E ï» ï» 46.23556°N 6.05528°E ï» 46.23556 6.05528 ATLAS logo ATLAS
, ATLAS experiment From Wikipedia , the free encyclopedia Jump to : navigation search ATLAS redirects here . For the linear accelerator , see Argonne Tandem Linear Accelerator System For other uses , see Atlas disambiguation Large Hadron Collider LHC LHC experiments ATLAS A Toroidal LHC Apparatus CMS Compact Muon Solenoid LHCb LHC-beauty ALICE A Large Ion Collider Experiment TOTEM Total Cross Section , Elastic Scattering and Diffraction Dissociation LHCf LHC-forward MoEDAL Monopole and Exotics Detector At the LHC LHC preaccelerators p and Pb Linear accelerators for protons Linac 2 and Lead Linac 3 not marked Proton Synchrotron Booster PS Proton Synchrotron SPS Super Proton Synchrotron Coordinates 46°14â²8â³N 6°3â²19â³E ï» ï» 46.23556°N 6.05528°E ï» 46.23556 6.05528 ATLAS logo ATLAS , Compact Muon Solenoid From Wikipedia , the free encyclopedia Jump to : navigation search Coordinates 46°18â²34â³N 6°4â²37â³E ï» ï» 46.30944°N 6.07694°E ï» 46.30944 6.07694 Large Hadron Collider LHC LHC experiments ATLAS A Toroidal LHC Apparatus CMS Compact Muon Solenoid LHCb LHC-beauty ALICE A Large Ion Collider Experiment TOTEM Total Cross Section , Elastic Scattering and Diffraction Dissociation LHCf LHC-forward MoEDAL Monopole and Exotics Detector At the LHC LHC preaccelerators p and Pb Linear accelerators for protons Linac 2 and Lead Linac 3 not marked Proton Synchrotron Booster PS Proton Synchrotron SPS Super Proton Synchrotron View of the CMS endcap through the barrel sections . The ladder to the lower right gives an impression of . scale The Compact Muon Solenoid CMS
, Compact Muon Solenoid From Wikipedia , the free encyclopedia Jump to : navigation search Coordinates 46°18â²34â³N 6°4â²37â³E ï» ï» 46.30944°N 6.07694°E ï» 46.30944 6.07694 Large Hadron Collider LHC LHC experiments ATLAS A Toroidal LHC Apparatus CMS Compact Muon Solenoid LHCb LHC-beauty ALICE A Large Ion Collider Experiment TOTEM Total Cross Section , Elastic Scattering and Diffraction Dissociation LHCf LHC-forward MoEDAL Monopole and Exotics Detector At the LHC LHC preaccelerators p and Pb Linear accelerators for protons Linac 2 and Lead Linac 3 not marked Proton Synchrotron Booster PS Proton Synchrotron SPS Super Proton Synchrotron View of the CMS endcap through the barrel sections . The ladder to the lower right gives an impression of . scale The Compact Muon Solenoid CMS , Tevatron From Wikipedia , the free encyclopedia Jump to : navigation search Coordinates 41°49â²55â³N 88°15â²06â³W ï» ï» 41.831904°N 88.251715°W ï» 41.831904 88.251715 Hadron colliders The Tevatron background and Main Injector rings Intersecting Storage Rings CERN 1971â1984 Super Proton Synchrotron CERN 1981â1984 ISABELLE BNL cancelled in 1983 Tevatron Fermilab 1987â2011 Relativistic Heavy Ion Collider BNL 2000âpresent Superconducting Super Collider Cancelled in 1993 Large Hadron Collider CERN 2009âpresent Super Large Hadron Collider Proposed , CERN 2019â Very Large Hadron Collider Theoretical The Tevatron was a circular particle accelerator in the United States at the Fermi National Accelerator Laboratory also known as Fermilab just east of Batavia , Illinois and is
, Tevatron From Wikipedia , the free encyclopedia Jump to : navigation search Coordinates 41°49â²55â³N 88°15â²06â³W ï» ï» 41.831904°N 88.251715°W ï» 41.831904 88.251715 Hadron colliders The Tevatron background and Main Injector rings Intersecting Storage Rings CERN 1971â1984 Super Proton Synchrotron CERN 1981â1984 ISABELLE BNL cancelled in 1983 Tevatron Fermilab 1987â2011 Relativistic Heavy Ion Collider BNL 2000âpresent Superconducting Super Collider Cancelled in 1993 Large Hadron Collider CERN 2009âpresent Super Large Hadron Collider Proposed , CERN 2019â Very Large Hadron Collider Theoretical The Tevatron was a circular particle accelerator in the United States at the Fermi National Accelerator Laboratory also known as Fermilab just east of Batavia , Illinois and is , Particle detector From Wikipedia , the free encyclopedia Jump to : navigation search Summary of Particle Detectors In experimental and applied particle physics nuclear physics and nuclear engineering a particle detector also known as a radiation detector is a device used to detect , track , and or identify high-energy particles such as those produced by nuclear decay cosmic radiation or reactions in a particle accelerator Modern detectors are also used as calorimeters to measure the energy of the detected radiation . They may also be used to measure other attributes such as momentum , spin , charge etc . of the . particles Contents 1 Description 1.1 Examples and types 1.2 Modern detectors 2 Installations of particle detectors 2.1 At colliders 2.2 Under construction 2.3 Without colliders
, Particle detector From Wikipedia , the free encyclopedia Jump to : navigation search Summary of Particle Detectors In experimental and applied particle physics nuclear physics and nuclear engineering a particle detector also known as a radiation detector is a device used to detect , track , and or identify high-energy particles such as those produced by nuclear decay cosmic radiation or reactions in a particle accelerator Modern detectors are also used as calorimeters to measure the energy of the detected radiation . They may also be used to measure other attributes such as momentum , spin , charge etc . of the . particles Contents 1 Description 1.1 Examples and types 1.2 Modern detectors 2 Installations of particle detectors 2.1 At colliders 2.2 Under construction 2.3 Without colliders Friday , Aug . 19, 2011 Subscribe Contact Fermilab Today Archive Classifieds Search Feature New Fermilab experiment to take muons out for a spin Fermilab's planned muon g-2 experiment will use the storage ring that was used in a previous muon g-2 experiment at Brookhaven National Laboratory . Members of the muon g-2 collaboration attended a meeting at Fermilab in March . Photo : Reidar Hahn A new experiment planned at Fermilab will allow researchers to peer into the sub-atomic world of virtual particles and resolve a decade old mystery . The Fermilab muon g-2 experiment will use an intense beam of muons , short-lived particles that are similar to electrons but 200 times . heavier One of the most important things about this experiment is that it will help guide what's found in the LHC and
Friday , Aug . 19, 2011 Subscribe Contact Fermilab Today Archive Classifieds Search Feature New Fermilab experiment to take muons out for a spin Fermilab's planned muon g-2 experiment will use the storage ring that was used in a previous muon g-2 experiment at Brookhaven National Laboratory . Members of the muon g-2 collaboration attended a meeting at Fermilab in March . Photo : Reidar Hahn A new experiment planned at Fermilab will allow researchers to peer into the sub-atomic world of virtual particles and resolve a decade old mystery . The Fermilab muon g-2 experiment will use an intense beam of muons , short-lived particles that are similar to electrons but 200 times . heavier One of the most important things about this experiment is that it will help guide what's found in the LHC and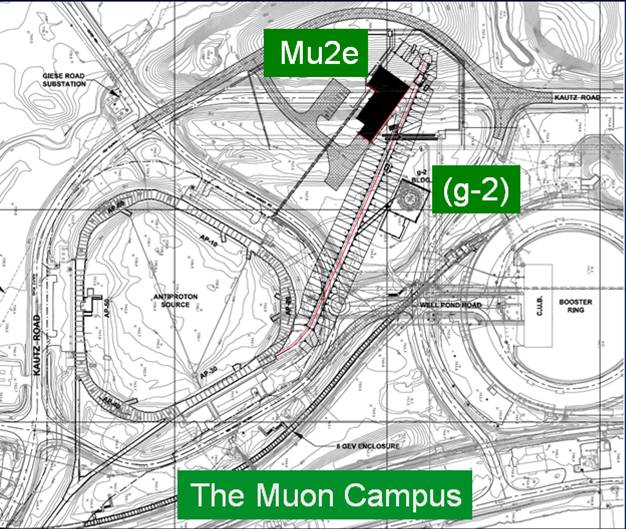 Home Fermi Home Acc . Division Home Phone Directory Run II Run IIb Please email comments problems Security , Privacy , Legal Page Last Updated Nov 29, 2011 Meetings Mu2e g-2 Photo Album Organizational Chart The name attribute has been replaced with id , but both have been used to account for older browsers On-Call Schedule Dept . Leave Calendar Muon E-Log secure E-log Archives Muon Rookie Book v2.0 Worklist Database Worklist Request Documents Projects Machine E-Logs Fermilab at Work Stockroom Catalog Accelerator Status Java Applications FTL Login On-site Only HTML Reference Page Lattice
Home Fermi Home Acc . Division Home Phone Directory Run II Run IIb Please email comments problems Security , Privacy , Legal Page Last Updated Nov 29, 2011 Meetings Mu2e g-2 Photo Album Organizational Chart The name attribute has been replaced with id , but both have been used to account for older browsers On-Call Schedule Dept . Leave Calendar Muon E-Log secure E-log Archives Muon Rookie Book v2.0 Worklist Database Worklist Request Documents Projects Machine E-Logs Fermilab at Work Stockroom Catalog Accelerator Status Java Applications FTL Login On-site Only HTML Reference Page Lattice , Radiation From Wikipedia , the free encyclopedia Jump to : navigation search For other uses , see Radiation disambiguation Illustration of the relative abilities of three different types of ionizing radiation to penetrate solid matter . Alpha particles α are stopped by a sheet of paper while beta particles β are stopped by an aluminium plate . Gamma radiation γ is dampened when it penetrates . lead In electromagnetic radiation such as microwaves from an antenna , shown here the term radiation applies only to the parts of the electromagnetic field that radiate into infinite space and decrease in intensity by an inverse-square law of power , so that the total radiation energy that crosses through an imaginary spherical surface is the same , no matter how far away from the antenna the
, Radiation From Wikipedia , the free encyclopedia Jump to : navigation search For other uses , see Radiation disambiguation Illustration of the relative abilities of three different types of ionizing radiation to penetrate solid matter . Alpha particles α are stopped by a sheet of paper while beta particles β are stopped by an aluminium plate . Gamma radiation γ is dampened when it penetrates . lead In electromagnetic radiation such as microwaves from an antenna , shown here the term radiation applies only to the parts of the electromagnetic field that radiate into infinite space and decrease in intensity by an inverse-square law of power , so that the total radiation energy that crosses through an imaginary spherical surface is the same , no matter how far away from the antenna the Quantum Diaries Thoughts on work and life from particle physicists from around the . world Home About Quantum Diaries Latest Posts All Blogs John Felde UC Davis USA View Blog Read Bio Latest Posts 2012.03.05 Fast Photosensors for Neutrino Physics 2011.11.22 Recent Events at UC Davis 2011.11.09 First Double Chooz Neutrino Oscillation Result USLHC USLHC USA View Blog Read Bio Latest Posts 2012.09.17 So long , and thanks for all the fish 2012.09.15 I don’t really like flying , but 2012.09.07 Why particle detectors need a trigger Frank Simon MPI for Physics Germany View Blog Read Bio Latest Posts 2012.07.04 Plus Two 2011.12.14 After the talk is before the talk 2011.10.24 Breathe Flip Tanedo USLHC USA View Blog Read Bio Latest Posts 2012.07.19 The Post-Higgs Hangover : where’s the new physics
Quantum Diaries Thoughts on work and life from particle physicists from around the . world Home About Quantum Diaries Latest Posts All Blogs John Felde UC Davis USA View Blog Read Bio Latest Posts 2012.03.05 Fast Photosensors for Neutrino Physics 2011.11.22 Recent Events at UC Davis 2011.11.09 First Double Chooz Neutrino Oscillation Result USLHC USLHC USA View Blog Read Bio Latest Posts 2012.09.17 So long , and thanks for all the fish 2012.09.15 I don’t really like flying , but 2012.09.07 Why particle detectors need a trigger Frank Simon MPI for Physics Germany View Blog Read Bio Latest Posts 2012.07.04 Plus Two 2011.12.14 After the talk is before the talk 2011.10.24 Breathe Flip Tanedo USLHC USA View Blog Read Bio Latest Posts 2012.07.19 The Post-Higgs Hangover : where’s the new physics The 21th Anniversary International Workshop on Vertex Detectors VERTEX 2012 The 21st International Workshop on Vertex Detectors will review the progress on silicon based vertex detectors . The workshop covers existing and future detectors , new , developments radiation hardness , simulation , tracking alignment , electronics , triggering , and applications to medical and other . fields It will be held between 16th and 21st Sept . 2012 at Seogwipo KAL Hotel in Jeju , . KOREA An-nyung-hwa-woo-gga An-nyung-hwa-woo-gga is Jeju Island dialect . It means Hello Proceedings The proceedings of the conference will be published in Proceedings of Science the open access online journal organized by SISSA , the International School for Advanced Studies based in Trieste . The proceedings will be
The 21th Anniversary International Workshop on Vertex Detectors VERTEX 2012 The 21st International Workshop on Vertex Detectors will review the progress on silicon based vertex detectors . The workshop covers existing and future detectors , new , developments radiation hardness , simulation , tracking alignment , electronics , triggering , and applications to medical and other . fields It will be held between 16th and 21st Sept . 2012 at Seogwipo KAL Hotel in Jeju , . KOREA An-nyung-hwa-woo-gga An-nyung-hwa-woo-gga is Jeju Island dialect . It means Hello Proceedings The proceedings of the conference will be published in Proceedings of Science the open access online journal organized by SISSA , the International School for Advanced Studies based in Trieste . The proceedings will be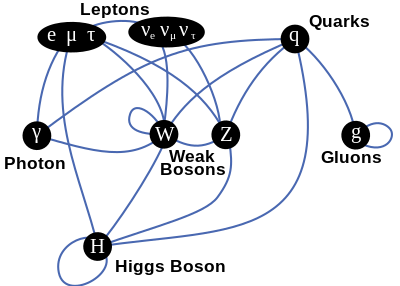 , Standard Model From Wikipedia , the free encyclopedia Jump to : navigation search This article is about the Standard Model of particle physics . For other uses , see Standard model disambiguation This article is a non-mathematical general overview of the Standard Model . For a mathematical description , see the article Standard Model mathematical formulation The Standard Model of elementary particles with gauge bosons in the rightmost . column Standard model of particle physics Large Hadron Collider tunnel at CERN Background Particle physics Standard Model Quantum field theory Gauge theory Spontaneous symmetry breaking Higgs mechanism Constituents Electroweak interaction Quantum chromodynamics CKM matrix Limitations Strong CP problem Hierarchy problem Neutrino oscillations See also :
, Standard Model From Wikipedia , the free encyclopedia Jump to : navigation search This article is about the Standard Model of particle physics . For other uses , see Standard model disambiguation This article is a non-mathematical general overview of the Standard Model . For a mathematical description , see the article Standard Model mathematical formulation The Standard Model of elementary particles with gauge bosons in the rightmost . column Standard model of particle physics Large Hadron Collider tunnel at CERN Background Particle physics Standard Model Quantum field theory Gauge theory Spontaneous symmetry breaking Higgs mechanism Constituents Electroweak interaction Quantum chromodynamics CKM matrix Limitations Strong CP problem Hierarchy problem Neutrino oscillations See also : , Gravitation From Wikipedia , the free encyclopedia Redirected from Gravity Jump to : navigation search This article is about the natural phenomenon . For other uses , see Gravitation disambiguation Gravity redirects here . For other uses , see Gravity disambiguation Law of Gravity and Laws of Gravity redirect here . For other uses , see Law of Gravity disambiguation Hammer and Feather Drop Apollo 15 astronaut David Scott on the Moon recreating Galileo's famous gravity experiment . 1.38 MB ogg Theora format Gravitation or gravity is a natural phenomenon by which physical bodies attract each other with a force proportional to their masses Gravitation is most familiar as the agent that gives weight to objects with mass and causes them to fall to the ground when dropped . Gravitation causes
, Gravitation From Wikipedia , the free encyclopedia Redirected from Gravity Jump to : navigation search This article is about the natural phenomenon . For other uses , see Gravitation disambiguation Gravity redirects here . For other uses , see Gravity disambiguation Law of Gravity and Laws of Gravity redirect here . For other uses , see Law of Gravity disambiguation Hammer and Feather Drop Apollo 15 astronaut David Scott on the Moon recreating Galileo's famous gravity experiment . 1.38 MB ogg Theora format Gravitation or gravity is a natural phenomenon by which physical bodies attract each other with a force proportional to their masses Gravitation is most familiar as the agent that gives weight to objects with mass and causes them to fall to the ground when dropped . Gravitation causes . Skip to Content Physics Department Search Physics Department California Polytechnic State University Navigation Our Department Home Department Mission and Assessment Why physics People Faculty Staff Students Teaching Faculty Office Hours Learning Center Hours Courses and Books Curriculum Research Faculty Projects Senior Projects Other Colloquiums Resources for students Alumni Astronomy Club and Observatory Society of Physics Students SPS Women in Physics Club Physics Department Faculty Thomas Gutierrez Dr . Thomas Gutierrez Tel : 805-756-2455 Email : tdgutier calpoly.edu Office : 25-223 Research interests : Neutrinoless double beta decay , nuclear and particle physics , quantum information Personal web page CP Home CP Find It Get Adobe Reader Microsoft Viewers Physics Department
. Skip to Content Physics Department Search Physics Department California Polytechnic State University Navigation Our Department Home Department Mission and Assessment Why physics People Faculty Staff Students Teaching Faculty Office Hours Learning Center Hours Courses and Books Curriculum Research Faculty Projects Senior Projects Other Colloquiums Resources for students Alumni Astronomy Club and Observatory Society of Physics Students SPS Women in Physics Club Physics Department Faculty Thomas Gutierrez Dr . Thomas Gutierrez Tel : 805-756-2455 Email : tdgutier calpoly.edu Office : 25-223 Research interests : Neutrinoless double beta decay , nuclear and particle physics , quantum information Personal web page CP Home CP Find It Get Adobe Reader Microsoft Viewers Physics Department , Speed of light From Wikipedia , the free encyclopedia Jump to : navigation search Lightspeed redirects here . For other uses , see Speed of light disambiguation and Lightspeed disambiguation Speed of light Sunlight takes about 8 minutes 19 seconds to reach the Earth based on the average distance Exact values Metres per second 299,792,458 Planck units 1 Approximate values kilometres per second 300,000 kilometres per hour 1,080 million miles per second 186,000 miles per hour 671 million astronomical units per day 173 Approximate light signal travel times Distance Time one foot 1.0 ns one metre 3.3 ns from geostationary orbit to Earth 119 ms the length of Earth's equator 134 ms from Moon to Earth 1.3 s from Sun to Earth 1 AU 8.3 min from nearest star to Sun 1.3 pc 4.2 years from the nearest
, Speed of light From Wikipedia , the free encyclopedia Jump to : navigation search Lightspeed redirects here . For other uses , see Speed of light disambiguation and Lightspeed disambiguation Speed of light Sunlight takes about 8 minutes 19 seconds to reach the Earth based on the average distance Exact values Metres per second 299,792,458 Planck units 1 Approximate values kilometres per second 300,000 kilometres per hour 1,080 million miles per second 186,000 miles per hour 671 million astronomical units per day 173 Approximate light signal travel times Distance Time one foot 1.0 ns one metre 3.3 ns from geostationary orbit to Earth 119 ms the length of Earth's equator 134 ms from Moon to Earth 1.3 s from Sun to Earth 1 AU 8.3 min from nearest star to Sun 1.3 pc 4.2 years from the nearest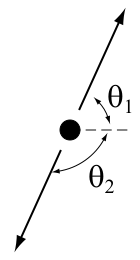 , Particle decay From Wikipedia , the free encyclopedia Jump to : navigation search Particle decay is the spontaneous process of one elementary particle transforming into other elementary particles . During this process , an elementary particle becomes a different particle with less mass and an intermediate particle such as W boson in muon decay The intermediate particle then transforms into other particles . If the particles created are not stable , the decay process can . continue Particle decay is also used to refer to the decay of hadrons However , the term is not typically used to describe radioactive decay in which an unstable atomic nucleus is transformed into a lighter nucleus accompanied by the emission of particles or radiation , although the two are conceptually . similar Note
, Particle decay From Wikipedia , the free encyclopedia Jump to : navigation search Particle decay is the spontaneous process of one elementary particle transforming into other elementary particles . During this process , an elementary particle becomes a different particle with less mass and an intermediate particle such as W boson in muon decay The intermediate particle then transforms into other particles . If the particles created are not stable , the decay process can . continue Particle decay is also used to refer to the decay of hadrons However , the term is not typically used to describe radioactive decay in which an unstable atomic nucleus is transformed into a lighter nucleus accompanied by the emission of particles or radiation , although the two are conceptually . similar Note